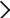About Fugaku
JapaneseThe system configuration of the supercomputer Fugaku is described below.
Total number of nodes
The total number of nodes in Fugaku is 158, 976.
A single CPU makes up a node, and two CPUs (two nodes) are mounted on a board called the CPU Memory Unit (CMU). Eight CMUs make up a "Bunch of Blades (BoB)," which means each BoB has 16 nodes. Three BoBs make up a Shelf, and therefore each Shelf has 48 nodes. Eight Shelves (384 nodes) are installed in a computer rack (some racks have 192 nodes). Fugaku is made up of 432 racks, of which 396 racks have 384 nodes, and 36 racks have 192 nodes. This makes a total of 158,976 nodes.
Peak Theoretical Performance
Fugaku can be run in a normal mode (CPU clock speed of 2 GHz) and a boost mode (CPU clock speed of 2.2 GHz), and the peak theoretical performance in each mode is summarized in the table below.
The high memory bandwidth is also one of the features of Fugaku.
| Peak performance Normal mode(CPU clock speed: 2 GHz) |
|
|---|---|
| Peak performance Boost mode (CPU clock speed: 2.2 GHz) |
|
| Total memory | 4.85 PiB |
| Total memory bandwidth | 163 PB/s |
Single node performance
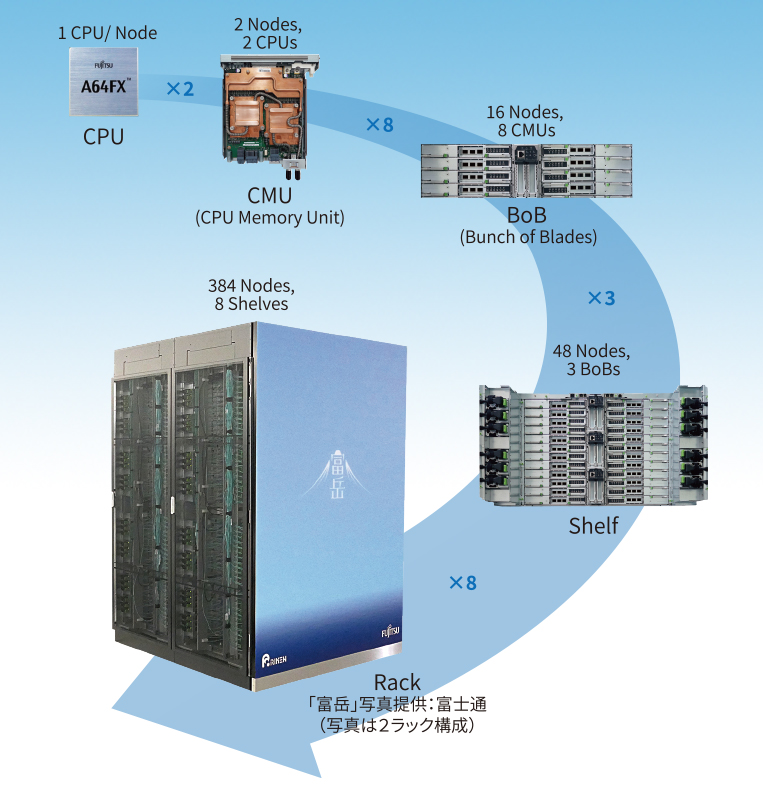
The single node performance is summarized below. The unique chip is based on the Arm instruction set architecture.
| Instruction set architecture | Armv8.2-A SVE 512 bit Fujitsu extension: hardware barrier, sector cache, prefetch |
|---|---|
| Number of core | 48 + 2 assistant cores 4 CMG (Core Memory Group, NUMA node) |
| Performance Normal mode (CPU clock speed: 2 GHz) |
Double precision: 3.072 TF; single precision: 6.144 TF; half-precision: 12.288 TF |
| Performance Boost mode(CPU clock speed: 2.2 GHz) |
Double precision: 3.3792 TF; single precision: 6.7584 TF; half-precision: 13.5168 TF |
| Cache *1 *2 | L1D/core: 64 KiB, 4way, 256 GB/s (load), 128 GB/s (store) L2/CMG: 8 MiB, 16way L2/node: 4 TB/s (load), 2 TB/s (store) L2/core: 128 GB/s (load), 64 GB/s (store) |
| Memory | HBM2 32 GiB, 1024 GB/s |
| Interconnect | Tofu Interconnect D (28 Gbps x 2 lane x 10 port) |
| I/O | PCIe Gen3 x16 |
| Technology | 7 nm FinFET |
- 1 Cache performance is with the CPU clock speed of 2 GHz
- 2 Please refer to GitHub
 for details
for details
CPU-Die (Image courtesy of Fujitsu)
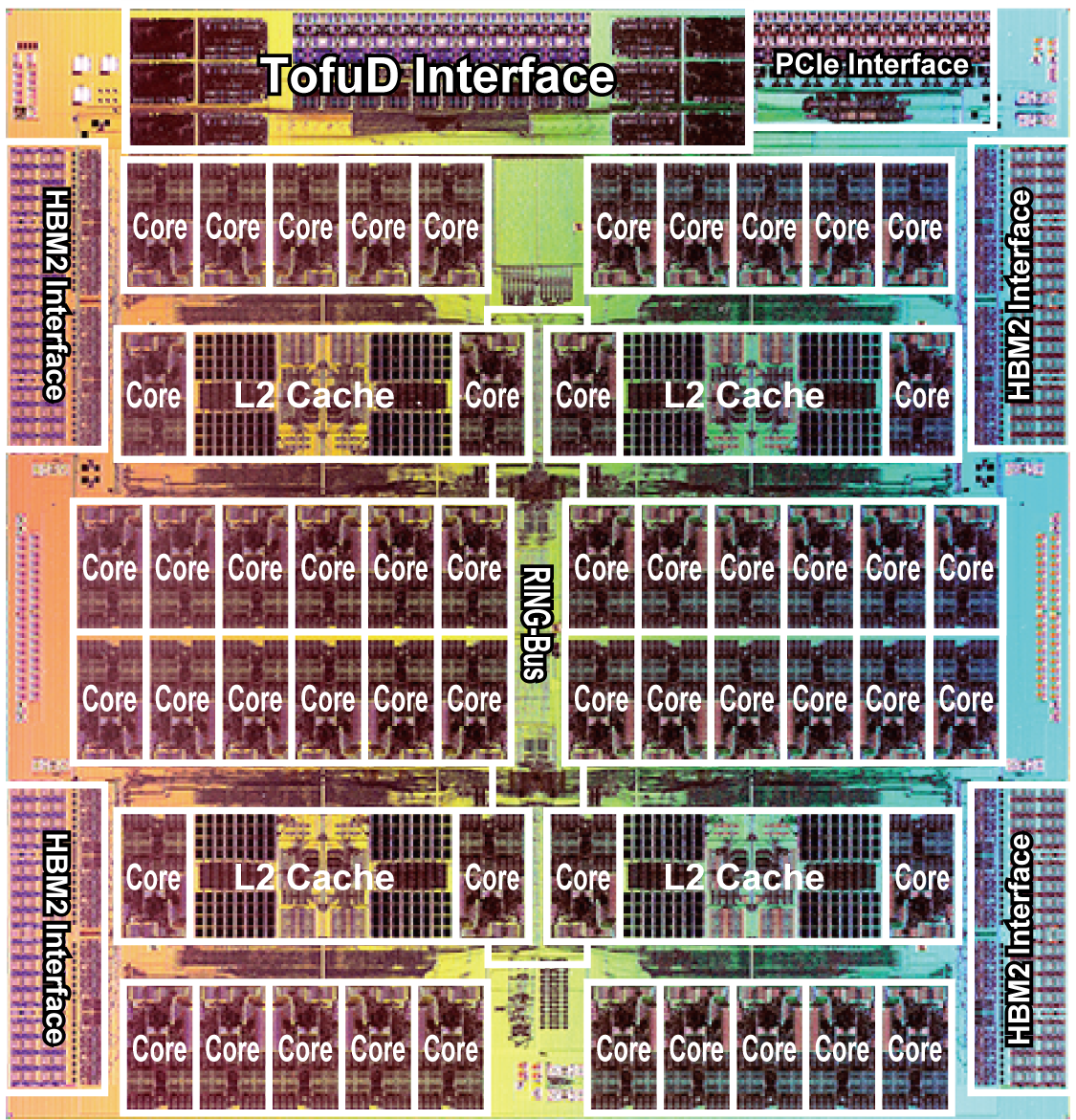
Tofu Interconnect D
The 6D mesh/torus interconnect is used for communication between nodes. Low latency and high throughput are achieved by Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA).
- Latency with 8 B input: 0.49 - 0.54 micro-sec
- Throughput with 1 MiB input: 6.35 GB/s
Six Tofu Network Interfaces (TNIs, each performs at 6.8 GB/s), 40.8 GB/s in total, are connected to the Tofu network router with 10 ports with 2 lanes each (20 lanes in total).
Tofu Cable
About 200,000 Tofu cables connect the CPUs of Fugaku. About half of them are fiber optic cables that run between racks, the total length of which is about 900 km.
| Number | Total length (m) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber optic cables | 97,632 |
855,101 |
| Electrical cables | 119,232 |
38,552 |
| Total | 216,864 |
893,653 |
Another approx. 10,000 cables connect the racks to the storage, etc.
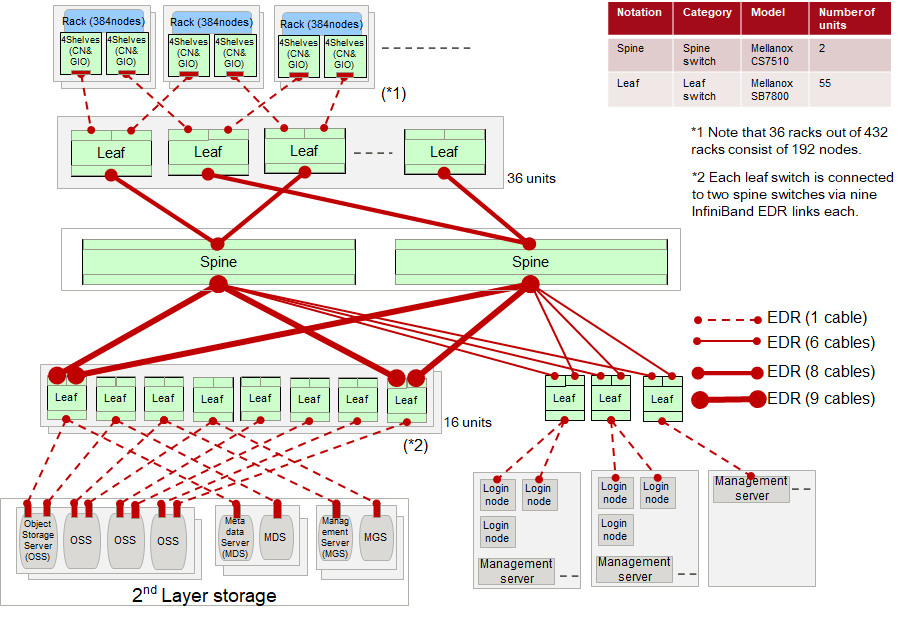
Storage
1st Layer
- LLIO (Lightweight Layered IO-Accelerator)
LLIO is a file system dedicated to the job execution area.
Providing the following three types of areas to the job.
・Node Temporary Area
・Shared Temporary Area
・Cache Area of 2nd Layer Storage
2nd Layer
- FEFS (Fujitsu Exabyte File System)
FEFS is a large shared area used by users and jobs.
Luster-based file system.
3rd Layer
- Commercial cloud storage services
I/O Network
Programming environment
| Compiler | Fortran 2008 and Fortran 2018 C11 with GNU and Clang extensions C++14 and C++17 with GNU and Clang extensions OpenMP 4.5 and OpenMP 5.0 Java |
|---|---|
| Parallel programing | XcalableMP [Details of XcalableMP (PDF 535 KB) FDPS [Details of FDPS (PDF 260 KB) |
| Script language | Python / Numpy / Scipy, Ruby |
| Numerical library | BLAS, LAPACK, ScaLAPACK SSL II (Fujitsu) EigenExa, Batched BLAS, 2.5D-PDGEMM |
System software
| Open-source management tool | Spack [Details of Spack (PDF 355 KB) |
|---|---|
| Container, virtual machine | Singularity, KVM |
| OS | Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 McKernel [Details of McKernel (PDF 641 KB) |
| MPI | Fujitsu MPI (Based on OpenMPI), MPICH-Tofu (Based on MPICH) [Details of MPICH-Tofu (PDF 404 KB) |
| File IO | LLIO DTF (Data Transfer Framework) [Details of DTF (PDF 220 KB) |