TOP
 Research
Research
 Research Teams
Research Teams
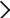 Computational Climate Science Research Team
Computational Climate Science Research Team
Computational Climate Science Research Team
Japanese
Team Principal Hirofumi Tomita
 htomita[at]riken.jp (Lab location: Kobe)
htomita[at]riken.jp (Lab location: Kobe)- Please change [at] to @
- 2025
- Team Principal, Computational Disaster Mitigation and Reduction Research Team, RIKEN R-CCS (-present)
- 2011
- Team Leader, Computational ClimateScience Research Team, AICS (renamed R-CCS in 2018), RIKEN (-present)
- 2007
- Senior Scientist, Research Institute of Global Change, JAMSTEC (fka Frontier Research Center for Global Change)
- 1999
- Researcher, Frontier Research Center for Global Change (fka Frontier Research System for Global Change)
- 1999
- Graduated from Graduate school of engineering, The University of Tokyo
Keyword
- High performance computing
- Climate modeling
Research summary
In climate simulations, combinations of numerical methods in models lead to large uncertainties of results. The necessary issues are to identify which part does cause the uncertainties and to estimate the inevitable uncertainties. To make such issues be easily resolved, our team develops the common library for computational climate science with high efficiency on high performance computers. The library systematizes various schemes, providing with model itself and analysis tools. At the same time, we will carry out pioneering works of large-scale climate computing. To do them, we are constructing the numerical schemes and reconsidering their theories by more principle than that in conventional models.
Main research results
Realistic expression of cumulonimbus clouds with a super-high-resolution simulation of the global atmosphere
The world’s first simulation of the global atmosphere with a horizontal resolution less than 1 km was performed using a global cloud-resolving model. This exceedingly high-resolution experiment enabled clouds such as cumulonimbus to be resolved using several grid cells in the model. When the grid size was reduced to less than 2 km, expression of the simulated cumulonimbi were improved and resembled the observed clouds. In other words, the clouds were explicitly resolved in the model. To examine the convergence of results from simulations with different horizontal grid-sizes and to evaluate uncertainty in the conclusions, further studies using a LES model with finer spatial resolution will be required.
Representative papers
- Kawai Y., and Tomita, H.:
“Numerical Accuracy Necessary for Large-Eddy Simulation of Planetary Boundary Layer Turbulence using Discontinuous Galerkin Method”
Mon. Weather. Rev., 151(6), 1479-1508 (2023). - Yanase, T., S. Nishizawa, H. Miura, and H. Tomita:
“Characteristic form and distance in high-level hierarchical structure of self-aggregated clouds in radiative-convective equilibrium”
Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 49, Issue 18, e2022GL100000 (2022). - Kawai, Y., and Tomita, H.:
"Numerical Accuracy of Advection Scheme Necessary for Large-Eddy Simulation of Planetary Boundary Layer Turbulence"
Mon. Weather. Rev., 149(9), 2993-3012 (2021). - Yanase, T., Nishizawa, S., Miura, H., Takemi, T., and Tomita, H.:
"New critical lenght for the onset of self-aggregation of moist convection"
Geophys. Res. Lett., 47, e2020GL088763 (2020). - Adachi, S. A. and Tomita, H.:
"Methodology of the constraint condition in dynamical downscaling for regional climate evaluation: A review"
J. Geophys. Res., 125 (11), e2019JD032166 (2020). - Sueki, K., Yamaura, T., Yashiro, H., Nishizawa, S., Yoshida, R., Kajikawa, Y., and Tomita, H.:
"Convergence of convective updraft emsembles with respect to the grid spacing of atmospheric models"
Geophys. Res. Lett., 46, 14817-14825 (2019). - Adachi, S. A., Nishizawa, S., Yoshida, R., Yamaura, T., Ando, K., Yashiro, H., Kajikawa, Y., and Tomita, H.:
"Contributions of changes in climatology and perturbation and the resulting nonlinearity to regional climate change"
Nature Communications, 8, 2224 (2017). - Sato, Y., Miura, H., Yashiro, H., Goto, D., Takemura, T., Tomita, H., and Nakajima, T.:
"Unrealistically pristine air in the Arctic produced by current global scale models"
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 26561 (2016). - Nishizawa, S., Yashiro, H., Sato, Y., Miyamoto, Y., and Tomita, H.:
"Influence of grid aspect ratio on planetary boundary layer turbulence in large-eddy simulations"
Geosci. Model Dev., 8, 3393-3419 (2015). - Miyamoto, Y., Kajikawa, Y., Yoshida, R., Yamaura, T., Yashiro, H., and Tomita, H.:
"Deep moist atmospheric convection in a sub-kilometer global simulation"
Geophys. Res. Lett., pp.4922–4926 (2013).
