5.4. Bulk Job¶
Bulk jobs can be submitted efficiently when the same execution module is executed multiple times while changing parameters.
It is also possible to execute jobs while changing input files in association with parameters. The job, executed per parameter, called sub job.
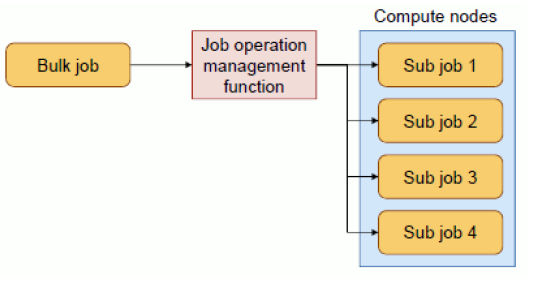
5.4.1. Job submission¶
--bulk option to pjsub command.--sparam option as the parameter to be passed to the sub job.[Style]
$ pjsub --bulk --sparam startbulkno-endbulkno
Option
Description
–bulk
Required option
–sparam
Required option
startbulkno
Specify the number (0 to 999999) to be assigned to the first sub job to be submitted.
endbulkno
Specify the number (0 to 999999) to be assigned to the last sub job to be submitted.
Attention
If specified at the same time with
--interact,--stepor--mswk, an error will occur if the specified option combination is invalid.
Example) When a bulk number from 0 to 9 is specified
[_LNlogin]$ pjsub --bulk --sparam "0-9" run.sh
In the above example, 10 sub jobs are started and parameters 0 to 9 are passed in increments of 1.
5.4.2. Bulk job script¶
The following is an example of a bulk job script.
Input data and output data are created so that each bulk number is included in the file name. In the job script, bulk numbers are handled with ${PJM_BULKNUM}.
When there are 10 types of data files from indata.0 to indata.9 and each of them is used as an input to execute a program
#!/bin/sh -x
#PJM -L "node=12"
#PJM -L "rscgrp=small"
#PJM -L "elapse=01:00:00"
#PJM --mpi "max-proc-per-node=4" # Maximum number of MPI processes created per node(*1)
#PJM -g groupname
#PJM -x PJM_LLIO_GFSCACHE=/vol000N
#PJM -S
#
IN_DATA=./indata.${PJM_BULKNUM} # $ {PJM_BULKNUM} expands to a bulk number
OUT_DATA=./outdata.${PJM_BULKNUM}
. _CNEnv_base
mpiexec --stdin ${IN_DATA} --of-proc ${OUT_DATA} ./a.out
5.4.3. Sub job ID¶
[Sub job ID example of bulk job]
Job ID |
Bulk number |
Sub job ID |
|---|---|---|
12345 |
1 |
12345[1] |
12345 |
2 |
12345[2] |
Note
If the job ID is “12345” and the bulk number is “1”, the sub job ID is “12345 [1]”.
5.4.4. Referencing job execution results¶
[Output file per sub job]
Style
Description
Job name.Sub job ID.out
Data written to the standard output by the sub job.
Job name.Sub job ID.err
Data written to the standard error output by the sub job.
Job name.Sub job ID.stats
This is the file to which the sub job statistical information is output.
[Output file per bulk job]
Style
Description
Job name.Sub job ID.stats
This is the file to which the statistical information of bulk jobs is output.
Attention
Job name is job script file name which specified with pjsub command.
If the job name starts with a single-byte number, the character “J” is added to the beginning of the output file name.
In the output file name, the job name part (including the letter “J” added at the beginning) is limited to 63 characters.
If a job is submitted from the standard input instead of a job script, the job name will be “STDIN”.
If standard output and standard error output are specified for the same job name for a bulk job, the output of each sub job is mixed.
Example) Bulk job execution result file name
sample.sh.i70990.stats # Bulk job statistics information file
sample.sh.e70990[0].err # Standard job output result file for sub job 0
sample.sh.i70990[0].stats # Sub job 0 statistical information output file
sample.sh.o70990[0].out # Sub job 0 standard output result file
sample.sh.e70990[1].err # Sub job 1 standard error output result file
sample.sh.i70990[1].stats # Sub job 1 statistical information output file
sample.sh.o70990[1].out # Sub job 1 standard output result file
sample.sh.e70990[2].err # Standard job output result file for sub job 2
sample.sh.i70990[2].stats # Sub job 2 statistical information output file
sample.sh.o70990[2].out # Sub job 2 standard output result file
Attention
If the target of output is not specified, it will be output in current directory of when executed pjsub.